Journal Description
Infectious Disease Reports
Infectious Disease Reports
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on infectious diseases published bimonthly online by MDPI (since Volume 12, Issue 3 - 2020).
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 34.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.1 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q2 (Infectious Diseases)
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Benefits of Publishing: We aim to be a leading journal on infectious diseases and to be in the top 20 journals listed in the Journal Citation Report (JCR) in this specific category in the near future.
Impact Factor:
2.4 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
2.2 (2024)
Latest Articles
Efficacy and Safety of Minocycline-Containing Bismuth Quadruple Therapies Versus Standard First-Line Bismuth Quadruple Therapies for Helicobacter pylori Eradication: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010016 - 6 Feb 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Background: Growing antibiotic resistance and the limited availability of key components in standard Helicobacter pylori treatments have driven the search for effective alternatives. Minocycline, with its broad-spectrum activity and favorable pharmacokinetics, has emerged as a promising substitute. This meta-analysis compares the safety and
[...] Read more.
Background: Growing antibiotic resistance and the limited availability of key components in standard Helicobacter pylori treatments have driven the search for effective alternatives. Minocycline, with its broad-spectrum activity and favorable pharmacokinetics, has emerged as a promising substitute. This meta-analysis compares the safety and efficacy of minocycline-containing bismuth quadruple therapy (MBQT) to conventional first-line BQT regimens, incorporating data from the recent study by Lin et al. Methods: The inclusion criteria were randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with a target population of both treatment-naïve and previously treated patients diagnosed with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection. The intervention received by eligible patients was a minocycline–bismuth quadruple therapy (MBQT) regimen containing bismuth, minocycline, proton pump inhibitors (PPI), and any additional antibiotic with a minimum period of 2 weeks of administration. We excluded study designs other than RCT and clinical trials that include patients without confirmed H. pylori infection, animal populations, in vitro experiments, and reports of other outcomes that did not include a minimum intervention duration of 2 weeks. A comprehensive literature search was conducted on PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, and ScienceDirect from inception to 20 May 2025. After screening via Rayyan, data were extracted on an Excel spreadsheet. Quality was assessed using the Cochrane RoB 2.0 tool. Eligible randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included and analyzed using RevMan 5.4. Outcomes assessed were intention-to-treat and per-protocol eradication rates. Adverse effects were compared among therapies. A random-effects model was used; an I2 < 50% and p-value < 0.05 indicated homogeneity and significant results respectively. Results: Five RCTs with 7 interventions involving 2812 patients were included. The pooled odds ratio (OR) for MBQT in intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis was 1.25 (95% CI: 0.96–1.61), showing a non-significant trend. No heterogeneity was detected (I2 = 0.0%). In the modified ITT (mITT) analysis (2 studies), MBQT showed higher eradication (OR: 1.70, 95% CI: 0.00–1042.90), but wide CI and high heterogeneity (I2 = 70.7%) limited interpretation. All studies were included in the per-protocol (PP) analysis, which showed a statistically significant improvement with MBQT (OR: 1.67, 95% CI: 1.14–2.45) and low heterogeneity (I2 = 5.2%), suggesting consistent results. Although not statistically significant, MBQT was associated with a slightly lower rate of adverse events compared to standard therapy (OR: 0.81, 95% CI: 0.59–1.12). I2 = 50.6% showed moderate heterogeneity in safety outcomes. Discussion: the number of included RCTs was modest, with only five studies meeting eligibility criteria, and only two contributing to the modified intention-to-treat analysis. The risk-of-bias assessment showed variation in methodological quality across the included studies. Several studies exhibited high risk judgments in critical domains. particularly randomization, deviations from intervention, and selective reporting. Patients who completed the treatment benefited more from MBQT, which also had a comparable safety profile to conventional BQT regimens. In the treatment of H. pylori infection, MBQT may be considered a safe alternative for first-line treatment.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Atypical Presentations in Melioidosis: A Case-Based Review from Endemic Regions
by
Saurav Jyoti Patgiri, Anukalpa Saikia, Sushmita Yadav, Md. Atique Ahmed, Luna Adhikari, Chimanjita Phukan, Chiranjay Mukhopadhyay and Harpreet Kaur
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010015 - 3 Feb 2026
Abstract
Background: Melioidosis, caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei, is a severe and often underdiagnosed infection endemic to South Asia, Southeast Asia, and northern Australia. While pneumonia and sepsis are the classical presentations, the disease is increasingly recognized for its diverse and atypical clinical manifestations.
[...] Read more.
Background: Melioidosis, caused by Burkholderia pseudomallei, is a severe and often underdiagnosed infection endemic to South Asia, Southeast Asia, and northern Australia. While pneumonia and sepsis are the classical presentations, the disease is increasingly recognized for its diverse and atypical clinical manifestations. Objective: The objective is to improve diagnostic accuracy and increase clinical awareness in both endemic and non-endemic settings by reviewing and classifying atypical presentations of melioidosis that have been documented in the literature. Methods: A narrative, case-based review was conducted using 238 published case reports and series from endemic and transitional regions during the period from 2000 to 2025. Cases with non-respiratory presentations or anatomical locations not commonly linked to melioidosis were classified as atypical. Clinical syndromes were used to classify the extracted cases, and common patterns in presentation, diagnosis, and outcome were examined. Results: One hundred and sixty published articles were included after a full text review. The most frequent atypical presentations included neurological involvement (e.g., brain abscess, encephalomyelitis), musculoskeletal infections (osteomyelitis, myositis), thyroid abscess, tubo-ovarian abscess, and dermatologic manifestations such as erythema nodosum. Imported and pediatric cases were also found. Numerous cases were misidentified as cancer, fungal infections, or tuberculosis. Among risk factors, diabetes mellitus was the most prevalent. Non-specific symptoms, a lack of laboratory capacity, and incorrect pathogen identification frequently resulted in delays in diagnosis. Conclusions: In endemic areas, melioidosis should be taken into account when making a differential diagnosis of a variety of clinical syndromes, especially in patients who have diabetes or have had relevant environmental exposure. Poor outcomes and diagnostic delays are greatly exacerbated by atypical presentations. Improving diagnostic capabilities and raising awareness are crucial to lessening the worldwide burden of this often ignored but potentially deadly infection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Review on Infectious Diseases)
Open AccessArticle
Invasive Fusariosis: Unusual Cases over 10 Years in a Tertiary Care Hospital and a Review of the Literature from Saudi Arabia
by
Hassan Almarhabi, Abdulmajeed Sarhan, Murad Essatari and Hassan Huwait
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010014 - 26 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Fusarium species are recognized as difficult-to-treat opportunistic pathogens due to extensive antifungal resistance and high mortality rates. Variability in its incidence and outcomes exists across different countries and centers. Large studies on Fusarium species are lacking in Saudi Arabia, with most
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Fusarium species are recognized as difficult-to-treat opportunistic pathogens due to extensive antifungal resistance and high mortality rates. Variability in its incidence and outcomes exists across different countries and centers. Large studies on Fusarium species are lacking in Saudi Arabia, with most previous publications being case reports. We describe all cases of invasive fusariosis identified at a tertiary center during a 10-year period and review previous reports in the country. Methods: A retrospective search of hospital records and the microbiology database was conducted to identify cases of invasive fusariosis among patients admitted during 2016–2025 at King Abdulaziz Medical City, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Results: Three cases of invasive fusariosis occurring over a 10-year period were identified. All cases occurred in the last three years of the study period. The incidence during those three years was 0.4 cases per 10,000 admissions per year. Clinical manifestations were fungemia in two immunocompetent patients and ulcers progressing to osteomyelitis in an immunocompromised patient. None of the patients progressed to death within 30 days of diagnosis. Conclusions: Data on Fusarium species are scarce in Saudi Arabia. Additional studies are required to better understand differences in invasive fusariosis between countries.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Demographic Factors and Trends Associated with Mortality After AIDS Diagnosis in Puerto Rico
by
Grisel Burgos-Barreto, Daniel Reyes and Raymond L. Tremblay
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010013 - 20 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background: Millions of people have died from AIDS-related illnesses since the start of the epidemic. The objective of this study is to determine the relationship between life years lost and demographic factors in the subset of individuals in Puerto Rico with advanced HIV
[...] Read more.
Background: Millions of people have died from AIDS-related illnesses since the start of the epidemic. The objective of this study is to determine the relationship between life years lost and demographic factors in the subset of individuals in Puerto Rico with advanced HIV disease, i.e., who received a diagnosis of AIDS, and to evaluate trends in poverty, age, and number of diagnoses and deaths over this timeframe. Methods: We identified 3624 individuals diagnosed with AIDS who received services under the Eligible Metropolitan Area (EMA) of San Juan, Puerto Rico, between 2000–2020, and correlated demographic factors with AIDS descriptive statistics using a retrospective cohort study design. We used socioeconomic characteristics to describe the population, estimated the life years lost (LYL) compared with the life expectancy of the general population of Puerto Rico at a given age as the null model, and evaluated the relationship of demographic variables with LYL, as well as trends in poverty and age/number of deaths/diagnoses over time. Results: More life years are lost with earlier AIDS onset, and there is also an association between LYL and the level of poverty, documented mode of transmission, and insurance status. LYL were higher among AIDS patients with lower income, with perinatal transmission, and among those without insurance in the age bracket of 40–49 years. No relationship between LYL and gender was detected. Moreover, over the years included in the timeframe of this study, certain trends emerged: we observed a greater proportion of AIDS to HIV diagnoses over time; HIV/AIDS diagnoses and deaths occurred on average at a higher age; the number of diagnoses per year initially rose over time and then declined; and the number of deaths per year as well as the poverty level in those diagnosed with HIV/AIDS increased over time. Conclusions: This study demonstrates the continued recent impact of the HIV epidemic specifically on those with advanced disease (AIDS), and further reaffirms the importance of treatment and prevention as well as demographic and social determinants of health, including age, poverty level, insurance status, and lifestyle, highlighting the disproportionate burden of HIV/AIDS among those with greater levels of poverty.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sexually Transmitted Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Addressing Infectious Diseases in Vulnerable Populations Under the Auspices of One Health: A Call for Action in Europe
by
Botond Lakatos, Ferenc Balázs Farkas, Giacomo Guido, Annalisa Saracino and Francesco Di Gennaro
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010012 - 15 Jan 2026
Abstract
While infectious diseases represent a daunting challenge to public health worldwide, their impact is disproportionately felt among the most vulnerable and marginalized segments of society [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Infections in Vulnerable Populations)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Diagnostic Accuracy of Utilizing Artificial Intelligence for Malaria Diagnostic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Icha Farihah Deniyati Faratisha, Khadijah Cahya Yunita, Hanifa Rizky Rahmawati, Loeki Enggar Fitri, Nuning Winaris and Lailil Muflikah
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010011 - 13 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background: Malaria remains a major public health concern around the world. Microscopic blood smear examination continues to be the gold standard for diagnosis; however, it requires high technical skills and expertise, limiting diagnostic accuracy in resource-poor settings. Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as
[...] Read more.
Background: Malaria remains a major public health concern around the world. Microscopic blood smear examination continues to be the gold standard for diagnosis; however, it requires high technical skills and expertise, limiting diagnostic accuracy in resource-poor settings. Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a promising tool to support malaria detection. This systematic review provides an overview of the diagnostic performance of AI-based systems for malaria diagnosis in a clinical setting. Methods: This study followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines and involved articles within the last 10 years that were collected from PubMed, ScienceDirect, Cochrane, EBSCO, and Wiley Online Library. Original articles that reported AI diagnostic accuracy with external validation were involved. The quality of each study was evaluated using the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS-2). Results: Ten studies with 6754 patients were analyzed. Pooled results of sensitivity [87.7% (95% CI: 78.2–93.4)] and specificity [91.4% (95% CI: 77.3–97.1)] revealed how much the AI agrees with each method when that method is used as a gold standard. Additionally, AI achieved a sensitivity of 87.7% and a specificity of 91.4% compared to microscopy examination and a sensitivity of 90.7% and a specificity of 88.3% compared to polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Conclusions: AI-based systems improve malaria diagnosis by providing high accuracy, automation, and lower costs. Showing performance comparable to reference methods such as microscopy and PCR, AI is a promising complementary tool for malaria control.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neglected Tropical Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Metabolomics in Infectious Diseases and Vaccine Response: Insights into Neglected Tropical and Non-Neglected Pathogens
by
Mahbuba Rahman, Hasbun Nahar Hera and Urbana Islam Barsha
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010010 - 12 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/objectives: Metabolomics has emerged as a powerful systems-biology tool for deciphering dynamic metabolic alterations occurring during infectious diseases and following vaccination. While genomics and proteomics provide extensive molecular and regulatory information, metabolomics uniquely reflects the biochemical phenotype associated with infection, immune activation, and
[...] Read more.
Background/objectives: Metabolomics has emerged as a powerful systems-biology tool for deciphering dynamic metabolic alterations occurring during infectious diseases and following vaccination. While genomics and proteomics provide extensive molecular and regulatory information, metabolomics uniquely reflects the biochemical phenotype associated with infection, immune activation, and immunometabolic reprogramming. The objective of this review is to provide an integrated analysis of metabolomics applications across both neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) and non-NTD pathogens, highlighting its dual role in biomarker discovery and vaccine response evaluation. Methods: A comprehensive literature-based synthesis was conducted to examine metabolomic studies in infectious diseases and vaccinology. Metabolic perturbations associated with specific pathogens, as well as vaccine-induced metabolic changes and correlates of immune responses, were systematically analyzed and compared across NTD and non-NTD contexts. Results: Distinct pathogen- and vaccine-associated metabolic signatures were identified, reflecting alterations in glycolysis, amino acid metabolism, lipid remodeling, and immunoregulatory pathways. Comparative analysis revealed both shared and disease-specific metabolic biomarkers across NTDs and non-NTD infections. Importantly, vaccine-related metabolic correlates were shown to mirror immune activation states and, in some cases, predict immunogenicity and response durability. Conclusions: This review bridges metabolomics research in infectious disease pathogenesis and vaccine immunology across the NTD and non-NTD spectrum. By integrating these domains, it introduces the concept of “metabolic immuno-signatures” as predictive and translational tools for evaluating vaccine efficacy and immune response outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Review on Infectious Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection in Romania Versus Europe: An Epidemiological and Public Health Perspective, 2024 Update
by
Andreea-Iuliana Ciobanu, Sebastian Ionescu, Ana Maria Tudor, Mariana Mărdărescu, Laurențiu-Mihăiță Stratan, Adrian Gabriel Marinescu, Cătălin Tiliscan, Aida-Isabela Adamescu, Oana Ganea, Sorin Ștefan Aramă and Victoria Aramă
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010009 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: This study presents a comprehensive and updated epidemiological and public health assessment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in Romania during 2022–2024, situated within the wider European context. Methods: For this retrospective descriptive study, we analyzed national surveillance data from the National Institute
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This study presents a comprehensive and updated epidemiological and public health assessment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in Romania during 2022–2024, situated within the wider European context. Methods: For this retrospective descriptive study, we analyzed national surveillance data from the National Institute of Infectious Diseases “Prof. Dr. Matei Balș” and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) reports, between 1985–2024, focusing especially on 2022–2024 period. Key indicators included incidence, mortality, transmission routes, age and gender distribution, and treatment coverage. Comparative analyses were performed between Romania and European Union (EU)/Eastern Europe data. Results: Between 1985 and 2024, Romania registered a cumulative total of 28,793 HIV cases, with 18,768 individuals living with HIV (PLHIV) as of 2024. In that year, 810 new HIV cases were diagnoses, indicating a modest uptick compared with 2022–2023. Heterosexual transmission continued to predominate (59.4%), followed by cases among men who have sex with men (MSM) (30.5%) and intravenous drug users (IDUs) (5.2%). Men represented more than three-quarters of all new infections. Mortality displayed considerable year-to-year variability, increasing from 125 HIV-related deaths in 2023 to 193 in 2024. Despite this, treatment coverage improved steadily, with 16,464 individuals receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) by the end of 2024. At 2.51 cases per 100,000 population, Romania’s incidence remained below the European average of 3.5 per 100,000. Nonetheless, the proportion of infections attributable to MSM transmission rose sharply—from 3.91% in 2007 to 32% in 2024—bringing Romania’s epidemiological profile increasingly in line with broader trends observed in Eastern Europe. Conclusions: These findings suggest that although Romania maintains a comparatively lower HIV incidence than the European average, the evolving transmission dynamics—most notably the substantial increase in MSM-related cases—signal a shifting epidemiological landscape that warrants strengthened, population-specific prevention measures and continued investment in comprehensive treatment and monitoring frameworks.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Persistence of Symptoms and Long-Term Recovery in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: Results from a Five-Year Follow-Up Cohort
by
Ana Roel Conde, Francisco Javier Membrillo de Novales, María Navarro Téllez, Carlos Gutiérrez Ortega and Miriam Estébanez Muñoz
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010008 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: This study aimed to determine the prevalence of persistent symptoms and the radiological and laboratory evolution at 6 months and 5 years after discharge in patients hospitalized for SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia during the first wave of the pandemic in Spain and to estimate
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This study aimed to determine the prevalence of persistent symptoms and the radiological and laboratory evolution at 6 months and 5 years after discharge in patients hospitalized for SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia during the first wave of the pandemic in Spain and to estimate the healthcare impact of their follow-up. Methods: A retrospective longitudinal observational study was conducted at the “Hospital Central de la Defensa”. A total of 200 patients aged >18 years with a diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia were screened. Clinical, radiological, and laboratory data were collected from electronic medical records. Patients with symptoms or radiological abnormalities at discharge underwent in-person evaluations, while the remainder were assessed by telephone. Results: A total of 182 patients met the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Of these, 112 were assessed in the outpatient setting; 60.7% required in-person evaluations, with normal pulmonary auscultation in 93.6%, complete radiological resolution in 85%, and normalized laboratory parameters in almost all cases. At 6 months, 26.5% presented at least one residual symptom, whereas only three patients (4.5%) reported symptoms at 5 years. No risk factors associated with symptom persistence were identified. The estimated cumulative healthcare cost was EUR 21,627.50. Conclusions: Among patients hospitalized for SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia during the first wave of the pandemic, 26.7% and 4.46% presented at least one persistent symptom at 6 months and 5 years after discharge, respectively.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Viral Infections)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEssay
Faster than Virus: The Physics of Pandemic Prediction
by
Serena Vita, Giovanni Morlino, Alessandra D’Abramo, Laura Scorzolini, Gaetano Maffongelli, Delia Goletti, Francesco Vairo, Enrico Girardi, Massimo Ciccozzi and Emanuele Nicastri
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010007 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background: Zoonotic spillover events with pandemic potential are increasingly associated with environmental change, ecosystem disruption, and intensified human–animal interactions. Although the specific origin and timing of future pandemics remain uncertain, there is a clear need to complement traditional preparedness strategies with approaches that
[...] Read more.
Background: Zoonotic spillover events with pandemic potential are increasingly associated with environmental change, ecosystem disruption, and intensified human–animal interactions. Although the specific origin and timing of future pandemics remain uncertain, there is a clear need to complement traditional preparedness strategies with approaches that support earlier anticipation and prevention. Objectives: This study aims to propose a conceptual approach to reframe pandemic preparedness toward proactive surveillance and spillover prevention. Methods: We introduce a tachyon-inspired conceptual approach, using a thought experiment based on hypothetical faster-than-light particles to illustrate anticipatory observation of pandemic emergence. The framework is informed by interdisciplinary literature on emerging infectious diseases, One Health surveillance, predictive epidemiology, and public-health preparedness. Results: The proposed approach highlights the importance of proactive, integrated surveillance systems that combine human, animal, and environmental data. Key elements include the use of advanced analytical tools such as neural networks, early characterization of population risk profiles, strengthened public-health infrastructure, coordinated governance, adaptable financial resources, and a resilient healthcare workforce. The integration of animal welfare considerations, translational research, and planetary health principles is emphasized as central to reducing spillover risk. Conclusions: Tachyon-inspired thinking offers a conceptual tool to support a shift from reactive pandemic response toward proactive anticipation and prevention. Embedding integrated surveillance and One Health principles into public-health systems may enhance early detection capacity and contribute to mitigating the impact of future pandemics.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Viral Infections)
Open AccessArticle
Beyond the Skin: Topical Amphotericin B Nanocarriers Targeting Cutaneous Leishmaniasis with Suppression of Lymphatic Parasite Burden
by
Francisco Alexandrino-Júnior, Gabriel Barcellos, Luiz Filipe Gonçalves-Oliveira, Luzia Monteiro de Castro Côrtes, Franklin Souza-Silva, Carlos Roberto Alves, Geovane Dias-Lopes, Juliana Figueiredo Peixoto, Beatriz Ferreira de Carvalho Patricio and Helvécio Vinícius Antunes Rocha
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010006 - 6 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) remains a global health challenge, with treatment options often limited by drug resistance and systemic toxicity. Amphotericin B (AmB) represents a promising alternative. but intravenous administration causes severe systemic adverse effects. Despite growing interest in topical therapies, knowledge gaps
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) remains a global health challenge, with treatment options often limited by drug resistance and systemic toxicity. Amphotericin B (AmB) represents a promising alternative. but intravenous administration causes severe systemic adverse effects. Despite growing interest in topical therapies, knowledge gaps remain regarding the comparative efficacy of delivery systems, including the influence of treatment timing and potential intrinsic effects. This study aimed to develop and characterize different topical AmB formulations (polymeric nanoparticles (PCL-AmB), a lipid-based (Oil_AmB) formulation, and a gel emulsion) to evaluate their in vivo efficacy against CL in a murine model, considering treatment initiation timing and potential intrinsic effects of the delivery systems. Methods: Formulations were prepared and characterized in terms of hydrodynamic size, polydispersity index, and AmB content. Antileishmanial activity was assessed in two independent in vivo experiments, with topical monotherapy administered five days per week for four weeks, starting either 10 or 30 days post-infection, representing early and established chronic stages of infection, respectively. Results: All formulations exhibited nanoscale dimensions and high homogeneity, with the lipid system demonstrating superior AmB solubilization. Both PCL-AmB and Oil_AmB reduced parasite load in the footpad, with Oil_AmB also reducing parasite load in draining lymph nodes. Conclusions: PCL-AmB and Oil_AmB reduced lesions and parasite burden in L. amazonensis-infected mice. Treatment timing was critical, with early Oil_AmB also reducing parasite loads in draining lymph nodes. These findings suggest that topical AmB formulations may provide a promising alternative for CL treatment, though further studies are required to optimize efficacy and administration schedules.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Neglected Tropical Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
An Unusual Case of Listeria monocytogenes-Associated Rhombencephalitis Complicated by Brain Abscesses in Italy, 2024
by
Maria Gori, Giorgia Orsani, Carlotta Ortelli, Erika Scaltriti, Luca Bolzoni, Luigi Vezzosi, Silvia Bianchi, Clara Fappani, Daniela Colzani, Antonella Amendola, Danilo Cereda, Laura Marzorati, Stefano Pongolini and Elisabetta Tanzi
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010005 - 4 Jan 2026
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Listeria monocytogenes (Lm) is an extremely rare cause of brain abscesses, accounting for 1–10% of neurolisteriosis cases reported in the literature, associated with high mortality (approximately 23%). Data on diagnosis, management, and treatment is scarce. We report a case of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Listeria monocytogenes (Lm) is an extremely rare cause of brain abscesses, accounting for 1–10% of neurolisteriosis cases reported in the literature, associated with high mortality (approximately 23%). Data on diagnosis, management, and treatment is scarce. We report a case of listerial brain abscesses in an elderly patient in Italy who experienced progressively worsening bilateral ptosis. Methods: Diagnostic evaluation included neuroimaging, blood cultures, and microbiological investigations, followed by antimicrobial treatment according to available evidence. The isolated Lm strain underwent whole genome sequencing. Dietary history was also collected. Results: Positive early blood cultures were pivotal in identifying Lm as the aetiological agent. Neuroimaging revealed brain abscesses consistent with neurolisteriosis. The clinical course was complicated by pneumonia and opportunistic co-infecting pathogens, and despite adequate treatment according to the available literature, the outcome was fatal. Genomic characterisation revealed that the patient was infected with an strain belonged to the sequence type 206 and clonal complex 14, described as hypervirulent. The patient reported consuming several foods known to be associated with an increased risk of listeriosis. Conclusions: This case highlights the challenges involved in diagnosing and managing listerial brain abscesses, particularly in elderly patients. Even when the primary central nervous system infection is under control, the prognosis may be significantly impacted by comorbid conditions and hospital-related complications rather than the infection itself. Our findings underscore the need for improved preventive strategies and targeted risk communication regarding high-risk foods, particularly among elderly populations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Bacterial Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Infective Endocarditis in a Tertiary Hospital in Porto—Is There Anything New?
by
Carolina Gomes, Isabel Gomes Abreu and Lurdes Santos
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010004 - 25 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: Infective endocarditis (IE) remains a severe and complex disease despite advances in diagnosis and treatment. The changing epidemiological profile, with an ageing population, has reshaped its presentation and management. This study describes the epidemiological, clinical and microbiological characteristics of IE at a
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Infective endocarditis (IE) remains a severe and complex disease despite advances in diagnosis and treatment. The changing epidemiological profile, with an ageing population, has reshaped its presentation and management. This study describes the epidemiological, clinical and microbiological characteristics of IE at a Portuguese tertiary referral hospital prior to the establishment of a multidisciplinary Endocarditis Team. Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted including all adult patients diagnosed with definite or possible IE according to the 2015 ESC criteria, admitted to ULS São João, Porto, between January 2019 and December 2023. Data were collected from electronic medical records and included demographic characteristics, comorbidities, microbiology, imaging, surgical indications and outcomes. Results: A total of 143 IE episodes were identified. Median age was 71 years, with a predominance of heterologous material-related infections (81%). Enterococcus faecalis, viridans group streptococci and coagulase-negative staphylococci were the most frequent pathogens. Surgical indication was present in 74% of cases, although surgery was not performed in 22% due to comorbidities or frailty, contributing to a high in-hospital mortality rate. Conclusions: This study provides a contemporary overview of IE in Portugal, reflecting an elderly, comorbid population and a predominance of prosthetic disease. The results highlight the need for multidisciplinary management and early surgical decisions, supporting the creation of Endocarditis Teams in tertiary centres.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceEditorial
Raising the Bar of PK/PD Target Attainment of Beta-Lactams in Daily Clinical Practice: An Effective Strategy to Overcome Resistance Development to Novel Beta-Lactams?
by
Milo Gatti and Federico Pea
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010003 - 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
The increase of infections caused by difficult-to-treat resistant (DTR) Gram-negatives is becoming an ever-growing remarkable issue for public health [...]
Full article
Open AccessCase Report
A Rare Case of Rhizomucor pusillus Infection in a 3-Year-Old Child with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Presenting with Lung and Brain Abscesses—Case Report
by
Yanko Pahnev, Boryana Avramova, Natalia Gabrovska, Yolin Dontcheva, Genoveva Tacheva, Krasimir Minkin, Hans Kreipe, Nadezhda Yurukova, Marin Penkov, Nikola Kartulev, Zdravka Antonova, Velichka Oparanova, Nadezhda Tolekova, Petia Moutaftchieva, Bogdan Mladenov, Plamena Hristova, Kaloyan Gabrovski, Svetlana Velizarova, Albena Spasova and Hristo Shivachev
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010002 - 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Invasive Mucormycosis (IM) is an extremely rare infection with a high mortality rate, caused by a group of fungi classified as Mucorales moulds. Rhizomucor pusillus is a saprophitic, thermophilic, and angioinvasive microorganism that grows and lives at about 45 °C and is usually
[...] Read more.
Invasive Mucormycosis (IM) is an extremely rare infection with a high mortality rate, caused by a group of fungi classified as Mucorales moulds. Rhizomucor pusillus is a saprophitic, thermophilic, and angioinvasive microorganism that grows and lives at about 45 °C and is usually found in different environmental spaces such as soil, air, water, food, and other organic matter. These features predispose the infection to wide dissemination, especially in immunocompromised patients and most often in children after chemotherapy for hematological malignancies (HMs). Mucormycosis in patients with hematologic malignancies and neutropenia represents between 0.07% and 4.29% of the concomitant diseases. IM can develop into an infection in different sites, but its most common manifestation is pulmonary, followed by rhino-orbital–cerebral and disseminated forms. In recent years, an increased morbidity rate has been associated with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, as cited in the literature. There are many publications with COVID-19-associated mucormycosis (CAM) cases. The present treatment protocol includes extensive and radical surgical debridement and systemic antifungal therapy with Liposomal Amphotericin B (L-AmB), Posaconazole, and Isavuconazole, either combined or as monotherapy. Despite these new treatment modalities, the mortality rate remains over 50%. We present a rare case of a 3-year-old child with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and systemic Rhizomucor pusillus infection, diagnosed on the occasion of lung and brain abscesses. The patient underwent lung and brain surgery and is recovering well with no further complications. The two-year follow-up period shows no signs of recurrence of the disease.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Retrospective Evaluation of the Clinical and Mycological Efficacy of 69% Nitric Acid, 1064 nm Nd:YAG Laser, and Their Combination in the Treatment of Trichophyton rubrum Onychomycosis over a 12-Month Follow-Up
by
Raquel García De La Peña, José María Juárez-Jiménez, João Miguel Costa Martiniano and Ana María Rayo Pérez
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2026, 18(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr18010001 - 20 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Onychomycosis is a common nail infection primarily caused by Trichophyton rubrum, posing therapeutic challenges due to poor antifungal penetration and high recurrence rates. Conventional treatments include topical and systemic antifungals, but novel approaches such as laser therapy and chemical agents
[...] Read more.
Background: Onychomycosis is a common nail infection primarily caused by Trichophyton rubrum, posing therapeutic challenges due to poor antifungal penetration and high recurrence rates. Conventional treatments include topical and systemic antifungals, but novel approaches such as laser therapy and chemical agents like nitric acid have emerged as promising alternatives or adjuncts. However, comparative evidence regarding the clinical and mycological efficacy of these treatments remains limited. Objectives: We aimed to assess and compare the clinical and mycological efficacy of three therapeutic modalities—69% nitric acid, 1064 nm Nd:YAG laser, and their combination—in the treatment of Trichophyton rubrum onychomycosis over a 12-month follow-up period. Methods: A prospective, comparative, observational study was conducted, assigning patients with confirmed onychomycosis to one of three treatment groups: nitric acid, Nd:YAG 1064 nm laser, or combination therapy. Clinical and mycological cure rates, mean time to clinical resolution, changes in Onychomycosis Severity Index [OSI] scores, and mycological relapse rates were assessed over a 12-month follow-up. Results: All three groups demonstrated significant improvement in both clinical and mycological cure rates, with the combination therapy yielding the most favorable outcomes in terms of response speed and durability. Laser and nitric acid monotherapies were also effective, though associated with lower cure rates and longer times to resolution. The relapse rate was lowest in the combination group. Conclusions: The combination of nitric acid and Nd:YAG laser appears to be a more effective therapeutic option for Trichophyton rubrum onychomycosis, offering superior clinical and mycological outcomes compared to monotherapies, with faster resolution and lower relapse rates. These findings suggest that combination therapy may optimize the management of this challenging nail infection.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Sex Differences in Outcomes of Critically Ill Adults with Respiratory Syncytial Virus Pneumonia: A Retrospective Exploratory Cohort Study
by
Josef Yayan and Kurt Rasche
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 151; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060151 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) pneumonia is an underrecognized cause of critical illness in adults. However, the influence of biological sex on intensive care unit (ICU) outcomes in this population remains unclear. Due to limited case numbers and incomplete covariate data, this study
[...] Read more.
Background: Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) pneumonia is an underrecognized cause of critical illness in adults. However, the influence of biological sex on intensive care unit (ICU) outcomes in this population remains unclear. Due to limited case numbers and incomplete covariate data, this study was designed as exploratory and hypothesis-generating. Methods: We conducted a retrospective exploratory cohort study using the MIMIC-IV database and identified 105 adult ICU patients with laboratory-confirmed RSV pneumonia. Clinical variables included sex, age, ICU length of stay, use of mechanical ventilation, and weaning status. Exploratory multivariable logistic regression was performed to assess associations with in-hospital mortality and weaning success, acknowledging substantial missingness of comorbidity data, severity scores, and treatment variables. This limited adjustment for confounding and statistical power. Results: Overall, in-hospital mortality was 33.3%. Mortality was significantly higher among women than men (51.6% vs. 7.0%; p < 0.001), although the absolute number of deaths in men was very small. In adjusted models, female sex (OR 14.6, 95% CI 1.58–135.3, p = 0.018), reflecting model instability due to sparse events, as well as longer ICU stay (OR 1.22 per day, p = 0.001) were independently associated with higher mortality. Female sex was also associated with lower odds of successful weaning (OR 0.07, 95% CI 0.01–0.63, p = 0.018). These effect estimates must be interpreted cautiously due to the very small number of deaths in men and the resulting wide confidence intervals. Age and ventilation duration were not significant predictors. Conclusions: In this preliminary ICU cohort, female sex and prolonged ICU stay were linked to higher mortality and lower weaning success in adults with RSV pneumonia. However, given the very small number of events—particularly among male patients—together with the modest sample size, limited covariate availability, and unstable effect estimates, the findings should be viewed as exploratory rather than confirmatory. Larger, well-powered, prospective multicenter studies are needed to validate and further characterize potential sex-related differences in outcomes of RSV-associated critical illness.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Viral Infections)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Beyond the Spike Glycoprotein: Mutational Signatures in SARS-CoV-2 Structural Proteins
by
Emil Tonon, Riccardo Cecchetto, Virginia Lotti, Anna Lagni, Erica Diani, Asia Palmisano, Marco Mantoan, Livio Montesarchio, Francesca Palladini, Giona Turri and Davide Gibellini
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 150; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060150 - 18 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: The continuous emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants represents a major public health concern. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) enables genomic surveillance, facilitating the detection and monitoring of mutations that impact viral evolution. Methods: In this study, full-length SARS-CoV-2 genomes were analyzed between February 2022 and
[...] Read more.
Background: The continuous emergence of SARS-CoV-2 variants represents a major public health concern. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) enables genomic surveillance, facilitating the detection and monitoring of mutations that impact viral evolution. Methods: In this study, full-length SARS-CoV-2 genomes were analyzed between February 2022 and March 2024 as part of routine genomic surveillance conducted in Verona, Italy. Mutations in the envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N) structural proteins were investigated. Only substitutions with a total prevalence of greater than 1% in the study dataset were considered. Results: A total of 178 mutations were identified across the three proteins (E: 16; M: 33; N: 129), of which 18 met the inclusion threshold (E: 3; M: 5; N: 10). Mutations were classified according to temporal dynamics as fixed, emerging, or transient. Throughout the study period, fixed mutations were consistently prevalent, emerging mutations appeared later but persisted with an ascending trend, while transient mutations displayed a single frequency peak before disappearing. Several mutations were reported with potential structural or functional relevance based on the existing literature, while others remain of unknown significance. Conclusions: The mutational patterns detected in this study broadly reflect global evolutionary trends of SARS-CoV-2. These findings emphasize the importance of continued genomic surveillance and underline the need for integrated experimental approaches to clarify the biological and epidemiological impact of poorly characterized mutations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Viral Infections)
►▼
Show Figures
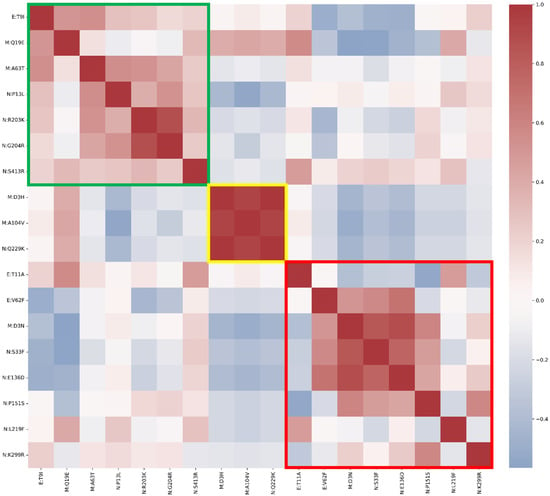
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Factors Associated with Condomless Anal Sex and Absence of Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) Use Among Brazilian Men Who Have Sex with Men: A Cross-Sectional Study
by
Laelson Rochelle Milanês Sousa, Patrícia Thais Cardoso da Silva, Allan Araujo Rodrigues, Márcio José dos Santos Silva, José Carlos Vinícius Jansen de Paz, Breno da Silva Oliveira, Daniel de Macêdo Rocha, Maria Wiklander, Elucir Gir and Renata Karina Reis
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 149; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060149 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Background: Men who have sex with men (MSM) in Brazil remain disproportionately affected by HIV. Combination prevention strategies, including Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP), are critical, yet adherence remains a challenge. This study aimed to identify factors associated with the simultaneous practice of condomless anal
[...] Read more.
Background: Men who have sex with men (MSM) in Brazil remain disproportionately affected by HIV. Combination prevention strategies, including Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP), are critical, yet adherence remains a challenge. This study aimed to identify factors associated with the simultaneous practice of condomless anal sex and non-use of PrEP among Brazilian MSM. Methods: A national cross-sectional study was conducted in 2020 via an online questionnaire disseminated on social media and dating apps. The outcome was defined as reporting condomless anal sex and no PrEP use in the previous year. Bivariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed. Results: Among 1357 MSM participants, a high proportion (69.4%) reported condomless anal sex without PrEP use. Factors significantly associated with this behavior included being younger (18–28 years; AOR: 2.59), identifying as homosexual (AOR: 6.04), bisexual (AOR: 5.30), or pansexual (AOR: 8.67), having a steady partner (AOR: 4.57), engaging primarily in receptive or insertive anal sex, and having a prior STI diagnosis (AOR: 1.49). Conclusions: The confluence of condomless sex and PrEP non-use reveals a significant vulnerability profile among young MSM in Brazil, even within steady relationships. These findings highlight the originality of examining this combined behavioral outcome and underscore the urgent need for targeted, culturally sensitive prevention strategies that address risk perception and enhance PrEP uptake to meet the UNAIDS 2030 goals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Containment Strategies of Infectious Diseases: Epidemiology, Surveillance and Prophylaxis)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceReview
The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence in Ocular Toxoplasmosis Detection: A Scoping Review on Diagnostic Models, Data Challenges, and Future Directions
by
Dodit Suprianto, Loeki Enggar Fitri, Ovi Sofia, Akhmad Sabarudin, Wayan Firdaus Mahmudy, Muhammad Hatta Prabowo and Werasak Surareungchai
Infect. Dis. Rep. 2025, 17(6), 148; https://doi.org/10.3390/idr17060148 - 8 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Ocular Toxoplasmosis (OT), a leading cause of infectious posterior uveitis, presents significant diagnostic challenges in atypical cases due to phenotypic overlap with other retinochoroiditides and a reliance on expert interpretation of multimodal imaging. This scoping review systematically maps the burgeoning application of artificial
[...] Read more.
Ocular Toxoplasmosis (OT), a leading cause of infectious posterior uveitis, presents significant diagnostic challenges in atypical cases due to phenotypic overlap with other retinochoroiditides and a reliance on expert interpretation of multimodal imaging. This scoping review systematically maps the burgeoning application of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly deep learning, in automating OT diagnosis. We synthesized 22 studies to characterize the current evidence, data landscape, and clinical translation readiness. Findings reveal a field in its nascent yet rapidly accelerating phase, dominated by convolutional neural networks (CNNs) applied to fundus photography for binary classification tasks, often reporting high accuracy (87–99.2%). However, development is critically constrained by small, imbalanced, single-center datasets, a near-universal lack of external validation, and insufficient explainable AI (XAI), creating a significant gap between technical promise and clinical utility. While AI demonstrates strong potential to standardize diagnosis and reduce subjectivity, its path to integration is hampered by over-reliance on internal validation, the “black box” nature of models, and an absence of implementation strategies. Future progress hinges on collaborative multi-center data curation, mandatory external and prospective validation, the integration of XAI for transparency, and a focused shift towards developing AI tools that assist in the complex differential diagnosis of posterior uveitis, ultimately bridging the translational chasm to clinical practice.
Full article
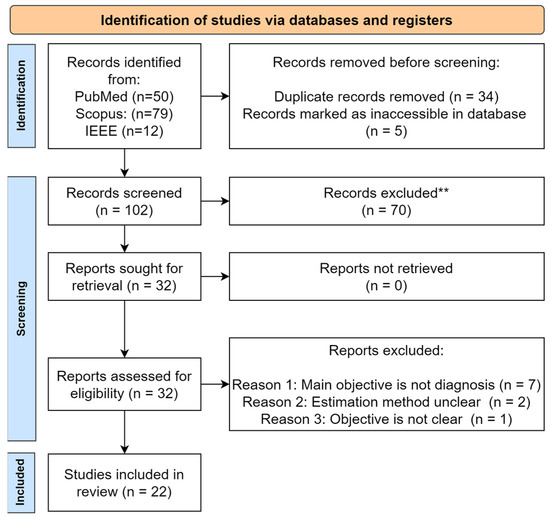
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Infectious Disease Reports, Insects, IJERPH, Pathogens, TropicalMed, Zoonotic Diseases
Vector-Borne Disease Spatial Epidemiology, Disease Ecology, and Zoonoses
Topic Editors: Chad L. Cross, Louisa Alexandra MessengerDeadline: 31 December 2026
Topic in
IJERPH, TropicalMed, Microorganisms, Infectious Disease Reports, Pathogens
Genetic, Environmental, and Climatic Drivers of Emerging Arboviruses and Public Health Implications
Topic Editors: André Ricardo Ribas Freitas, Pedro María Alarcón-Elbal, Luciano Pamplona de Góes CavalcantiDeadline: 20 January 2027
Topic in
Diseases, Epidemiologia, Infectious Disease Reports, Medicina, TropicalMed
Surveillance Systems and Predictive Analytics for Epidemics
Topic Editors: Georgia Kourlaba, Elisavet StavropoulouDeadline: 31 January 2027

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Infectious Disease Reports
Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of Healthcare-Associated Infections
Guest Editor: Emine Alp MeşeDeadline: 31 May 2026
Special Issue in
Infectious Disease Reports
Challenges in the Management of Onychomycosis and Other Superficial Fungal Infections
Guest Editor: Aditya K. GuptaDeadline: 30 June 2026
Special Issue in
Infectious Disease Reports
Infections in Vulnerable Populations
Guest Editors: Botond Lakatos, Francesco Di GennaroDeadline: 30 June 2026
Special Issue in
Infectious Disease Reports
Review on Infectious Diseases
Guest Editor: Carlo TasciniDeadline: 1 July 2026












